barrel compression test sternal fracture|sternal fracture death rate : advice Allen Test, Hyperabduction Syndrome Test: Examination type: Neurological : Patient . WEBDefinition: A bar (symbol: bar) is a metric unit of pressure that is defined as exactly 100,000 pascals (symbol: Pa). It is equal to 0.987 atmospheres (101,325 Pa), the unit often used as a reference of standard pressure. History/origin: The unit, bar, was introduced by Vilhelm Bjerknes, a Norwegian meteorologist who founded modern weather .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBPlaca Início de pista dupla A-42a, este sinal alerta o início de pista dupla com sentidos opostos, estas separadas por um canteiro ou um obstáculo central. Características: Placa de Advertência; Formato: Quadrado; .
Positive Test: Positive if pain or guarding is elicited. Interpretation: Positive test indicated possible rib fracture. Common errors in performing exam: Not compressing with enough force; not asking about location and type of pain if elicited; not examining in all possible positionsAllen Test, Hyperabduction Syndrome Test: Examination type: Neurological : Patient .Empty Can Test: Examination type: Muscle test (strength) Patient & Body Segment .Past Pointing Test: Examination type: Cognitive function, coordination .
Underlying shoulder or elbow pathology may make this test difficult to perform. .
Finger-Thumb Test: Examination type: Cognitive function, coordination .
Anatomical Snuff Box Compression Test. Phalen's Test or Wrist Press Test. Tinel .
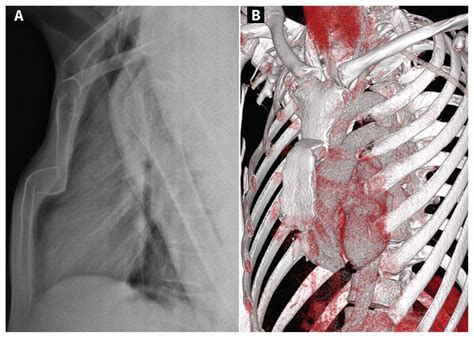
Halstead's Test: Examination type: Neurological, Vascular integrity: Patient .Medial Compression Test. Jerk Test of Hughston. Pivot Shift Test. Posterior .
Anterior Instability Test: Other Names: Leffert’s Test: Examination type: Joint .Performing the Test The examiner should the hand grasping the forearm move the .
Sternal fracture primarily results from blunt anterior chest-wall trauma and deceleration injuries and have an incidence of 3% to 6.8% in motor vehicle collisions. Athletic .
A portable CXR is often the first imaging test obtained in the trauma bay and is typically unremarkable in a patient with isolated sternal fracture. Ultrasonography is a rapid and .Patients with sternal fractures present with acute sternal pain, aggravated by deep breathing and coughing, associated with localized tenderness and signs of respiratory insufficiency. These .Episode Overview. Differentiate chest wall injury, rib fracture, and flail chest. Describe the clinical presentation and management of a sternal fracture. Describe Injuries to lung parenchyma: .
Sternal Fracture present on imaging. CT angiogram chest with contrast (if not already given IV contrast in prior imaging). Include CT angiogram of neck if known concurrent 1st rib fx. Monitor .Early thorough clinical assessment is essential while approaching a patient with suspected isolated sternal fracture to exclude associated injuries. sternal fracture if no other injuries . Sternal fractures are predominantly associated with deceleration injuries and blunt anterior chest trauma. Sternal trauma must be carefully evaluated by monitoring of vital .
Abstract. Purpose. Combined sternal and spinal fractures are rare traumatic injuries with significant risk of spinal and thoracic wall instability. Controversy remains with . Traumatic sternal fractures are rare injuries. The most common mechanism of injury is direct blunt trauma to the anterior chest wall. Most (> 95%) sternal fractures are .Rib fracture; Joint dysfunction (sternocostal, costovertebral, or costotransverse) Intercoastal Muscle Strain; Pertinent Negatives. DATA. TAGS. . Anterior to posterior force applied directly to the sternum during the sternal compression test will mobilize the structures of the chest that are in direct contact with the sternum. This is likely . Because sternal fractures are most commonly a result of trauma, initial treatment is often done by emergency medical professionals. However, once at the hospital, your doctor will take an X-ray .
Compression fractures can happen to any part of your spine, but they usually occur in the thoracic spine (middle section). Osteoporosis is a common cause of compression fractures, in addition to trauma (like after an .A sternal fracture is a fracture of the sternum (the breastbone), located in the center of the chest.The injury, which occurs in 5–8% of people who experience significant blunt chest trauma, may occur in vehicle accidents, when the still-moving chest strikes a steering wheel or dashboard [1] or is injured by a seatbelt. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), has also been known to . Friction plays an important role in metal forming operations. Therefore, many techniques are developed for evaluation of friction in large deformation processes.Among them the “Barrel Compression Test” (BCT) is a very simple method that quantitatively evaluates the constant friction factor, m, simply by compressing a cylindrical specimen.BCT was analyzed by .Compression Fractures of the Spine - Learn about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment from the MSD Manuals - Medical Consumer Version. . X-rays X-Rays An x-ray is an imaging test that takes a picture of the inside of your body. It uses a low dose of x-ray radiation. X-rays show body parts according to how dense (solid) they are .
PROGNOSIS AND COMPLICATIONS. Sternal fractures can either occur in isolation, or with other associated injuries. Prognosis is excellent for isolated sternal fractures, with most patients recovering completely over a period of weeks (average 10.4 weeks).[] The overall mortality of sternal fractures is 0.7%.[] However, two-thirds of sternal fractures have . The vast majority of transverse sternal fractures are isolated injuries and can be successfully treated; they will heal, with conservative management. 1,4,6,21 The main indication for surgical intervention after an acute sternal fracture is fracture displacement, fracture instability, associated chest trauma, and associated polytrauma injuries .
Sternal fracture–associated mortality can result from cardiac contusion, aortic rupture, pulmonary contusion, and thoracic spine compression fractures. Sternal and rib fractures are common concomitant injuries. In a retrospective study by Choi et al, of 475,710 adults admitted with rib fractures, 24,594 (5%) also had sternal fractures.
INTRODUCTION. Sternal fracture results from direct impact to the anterior chest wall; it occurs in 4% of motor vehicle crash (MVC) victims and 3%–8% of blunt thoracic trauma cases.[1,2] Sternal fracture is usually associated with high-energy trauma, as a consequence of a significant direct external force or as a result of vertebral compression and flexion of the chest.[]The sternum is also called the breastbone. Most broken sternums are caused by car crashes. In most cases, a broken sternum will heal on its own. It can take 3 months or longer for the pain to go away. The doctor has checked you carefully, but problems can develop later. If you notice any problems or new symptoms, get medical treatment right away. INTRODUCTION — . Multiple vital thoracic structures are at risk of injury from blunt chest trauma such as rapid deceleration and direct injury. Major concerns include chest wall injury (eg, rib fractures or flail chest), cardiovascular injury (eg, blunt aortic injury [BAI] or cardiac contusion), and pulmonary injury (eg, pneumothorax, contusions, or lacerations). Common mechanisms of blunt thoracic injury include motor vehicle collisions and falls. Chest wall injuries include rib fractures and sternal fractures; treatment involves supportive care, multimodal analgesia, and pulmonary toilet. Pneumothorax, hemothorax, and pulmonary contusions are also common and may be managed expectantly or with tube thoracostomy as .
S22.2 is a non-billable diagnosis code for fracture of sternum, use codes with a higher level of specificity: S22.20, S22.20XA, S22.20XB, S22.20XD, S22.20XG, . They will also likely order an x-ray or other imaging test to see if your bone is broken. . S22.000D Wedge compression fracture of unspecified thoracic vertebra, . Sternal fractures are rare accounting for about 3–8% of traumatic chest. There are many lines of treatments for sternal fractures which can be classified as conservative or surgical. Surgical techniques include wire fixation . Sternal fractures are rare injuries with an incidence of less than 0.5% of all fractures and an estimated 3–8% in blunt trauma patients [1,2,3,4].Traumatic sternal dislocations occur even less frequently [].The most common mechanism of injury is direct blunt trauma to the anterior chest caused by motor vehicle accidents [1, 6,7,8].The incidence of sternal injury has .
Sternal fractures in blunt chest trauma: a practical algorithm for management. Am J Emerg Med. 1997;15:252-5. 2. Retrospective study (n=33) of sternal fracture and relationship to BCI. Sternal fracture is not a marker for BCI. Management of sternal fracture should be directed at management of associated injuries. Fulda GJ . 1997 Sternal fractures typically result from the chest striking the steering wheel, with most injuries occurring in older vehicles lacking airbag deployment. These fractures are slightly more prevalent in women than men. Sternal fractures are more common in older patients, which appears to be due to the elastic chest wall of younger patients.
Education video describing the types of sternal fractures. Fractures of the sternum are fractures to the bone located in the center of the chest. These injur.Introduction. From the end of the 19th century up to the mid of the 20th century, fractures of the sternum were mentioned with an incidence of under 1% and increased with the number of car accidents to 5–8% of all bone injuries (1-6).The number is even higher in multiple trauma patients (3.9% isolated sternum fractures) in combination with other rib fractures (7.8–11.2%) and in .
Mortality is also associated with vertebral fractures, as women diagnosed with a compression fracture of the spine have a 15% higher mortality rate than those who do not experience fractures. 1 Riggs, B.L. and L.J. Melton, 3rd, "The worldwide problem of osteoporosis: insights afforded by epidemiology," Bone, 1995, 17(5 Suppl): p. 505S-511S. A Sternum fracture is a break of the breastbone in the middle of the chest. In more severe cases it dislocates at the sternoclavicular joint. Advert. Sternum fracture symptoms. Symptoms of a fractured sternum include: Sudden onset of pain at the front of the chest after an impact or fall of some kind;
conrad vochtmeter
Sternal fractures: a retrospective analysis of 272 cases. J Trauma 1993;35(1): 46-54. 6. Hossain M, Ramavath A, Kulangara J, Andrew JG. Current management of isolated sternal fractures in the UK: time for evidence based practice? A cross-sectional survey and review of literature. Compression of the chest wall can result in contusions, lacerations, rib or sternal fractures, solid organ injury, and overpressure injuries (e.g., pneumothorax) [11, 12]. . Sternal fractures may not be apparent on axial images when a horizontal sternal fracture is in the same plane as the CT cut . Therefore, to assess for sternal fracture .
Osteoporotic compression fractures are the most common red flag in the vertebral spine with a prevalence of 25% in women over the age of 65 and 40% over the age of 80. According to Langdon et al. (2010), the closed-fist percussion test has a sensitivity of 87,5% and a specificity of 90% in the detection of symptomatic fractures of the spine. The priority of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is to re-establish systemic blood flow by chest compression (CC), achieving threshold levels of coronary perfusion pressure (CPP) for successful resuscitation.1 Current guidelines identify the middle of the chest, and more specifically the lower sternal half, as the recommended point to perform CC. However, the . Although an important injury of chest trauma is rib fractures, other bone structures in the thorax should also be considered. Sternal fractures are usually caused by anterior blunt chest trauma of the steering wheel as a result of motor vehicle accidents.67 Sternal fractures may cause vascular injury, as well as pulmonary and myocardial contusions.
web25 anos. Com local. 3 reviews. Centro, Caratinga - MG. Sua busca acaba aqui. Seja bem-vindo ao meu perfil Cavalheiros, Deixe-me apresentar. Sou uma Acompanhante de Luxo com os seios mais lindos que você vai ver, Tenho lábios carnudos, Pele morena macia, Cheirosa e bronzeada da cor do Pecado, Bumbum empinado e lisinho, Cabelos grandes .
barrel compression test sternal fracture|sternal fracture death rate